Methodology and profile of survey respondents of Macao Tourist Satisfaction Index (MTSI)
Methodology
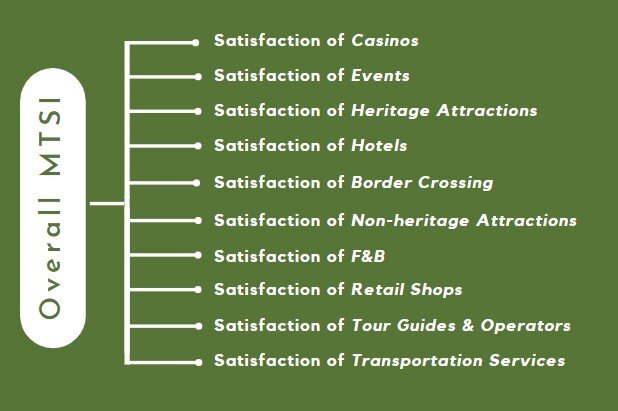
The Macao Tourist Satisfaction Index (MTSI) estimates visitors’ satisfaction based on their experience with ten tourism-related sectors or services in Macao. Sectors included in the index are (a) casinos, (b) events, (c) heritage attractions, (d) hotels, (e) border crossing, (f) non-heritage attractions, (g) F&B, (h) retail shops, (i) tour guides & operators, and (j) transportation services. Data are collected at each quarter of the year beginning from the third quarter of 2009. Starting in 2018, approximately 50 interviews are conducted per quarter for each sector which is equivalent to about 200 interviews per year per sector. Respondents are selected and interviewed based on a systematic sampling technique. Interviews are conducted at major sites including the Border Gate, Qingmao Checkpoint, ferry terminals, Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macao Bridge, Airport, the A-Ma Temple, Ruins of St. Paul’s, Senado Square, Rua do Cunha at Taipa, and the Cotai Strip.
The instrument used in the MTSI study is adopted from the American Customer Satisfaction Index (ACSI) model based on Fornell et al. (1996). Tourist satisfaction (TS) for each sector is assessed as a latent variable with three indicators, namely: (1) confirmation of expectations, (2) comparison with the ideal and (3) overall satisfaction. Each indicator is measured by an 11-point scale ranging from 0 to 10. The weight of each of the sector TS indicator is estimated based on structural equation modeling with maximum likelihood estimator. The estimated weights are used to construct the sector TSI value which is transformed to a 0- to 100-point scale: The higher the index, the more satisfied the tourists for the corresponding sector. The Overall MTSI is an average of the ten sector TSIs.
Note: Data collection in Q1 and Q2 2020 were suspended due to COVID-19 pandemic control measures.
General Model for Macao overall TSI
Reference
Fornell, C., M. D. Johnson, et al. (1996). "The American Customer Satisfaction Index: Nature, purpose, and findings." Journal of Marketing 60(4): 7.
THEORETICAL UNDERPINNING
The theoretical framework, methodological foundation and validity of the MTSI is grounded on the American Customer Satisfaction Index (ACSI) by Fornell (1996), and the work of Prof. Haiyan Song and his team at the Hong Kong Polytechnic University, adapting it for use in the tourism sector . A substantial body of work has followed since the first publication of the ACSI with many industries, business publications and a number of growing countries adopting and accepting the framework. Companies use ACSI-based estimates of their own customers’ satisfaction and benchmark this with national, intra-industry, and competitor indices, as a competitive and service differentiation tool. The Hong Kong Polytechnic School of Hotel and Tourism, led by Prof. Haiyan Song, modeled a similar index for Hong Kong’s tourism industry, which they term the PolyU TSI. The Macao TSI project was conceived as a collaboration between the PolyU TSI and ITRC with the view that regional comparisons can be made between Hong Kong and Macao in terms of tourist satisfaction, and, hopefully, with other regional destinations in the future.
Profile of survey respondents
The Macao Tourist Satisfaction Index (MTSI)
Research team: Leonardo (Don) A.N. Dioko, Phd., Wendy Tang, Patrick Lo and Janice Leong
The MTSI is a year-round survey that monitors the satisfaction of visitors to Macao in respect of several key tourism service sectors. Results of the MTSI are published quarterly and annually. Special focus reports are also issued occasionally.